






Creatine is a powerhouse supplement for boosting athletic performance and building muscle, but choosing between powder and capsules can be confusing.
In this article, we break down the surprising differences between these two forms, guiding you to the one that will best amplify your fitness results.
Get ready to discover which creatine form will take your gains to the next level, backed by cutting-edge research and expert insights.
A study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition confirms that creatine supplementation significantly enhances muscle strength and performance, making it a staple in many athletes' routines.
Now that we've introduced the topic of creatine supplementation, let's dive into the key differences between creatine powder and capsules to help you make the best choice for your fitness goals.
When considering creatine supplementation, understanding the differences between creatine capsules and powder is essential.
Creatine Capsules: Creatine capsules provide a convenient and flavorless method for creatine supplementation.
However, they tend to be pricier and are absorbed more slowly than powder.
Creatine Powder: Creatine powder is a budget-friendly, adaptable choice that permits dosage adjustments.
Nonetheless, it demands more preparation time and may not be as easily portable as capsules.
Below is a chart that summarizes the main differences between creatine powder and capsules.
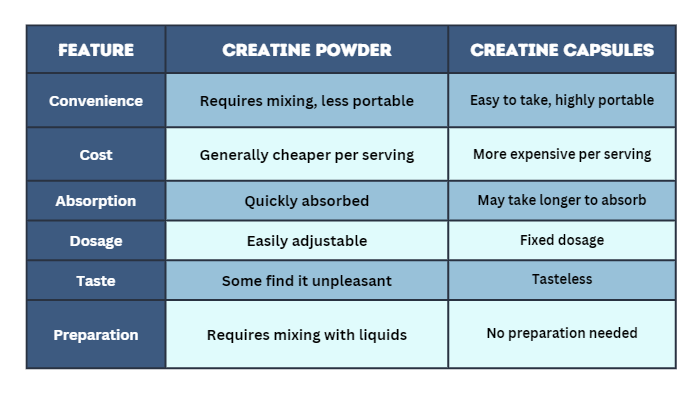
This study provides a more detailed comparison of the absorption rates of different forms of creatine.
Before we dive into the differences between creatine powder and capsules, let’s first understand what creatine is and why it’s so important for your body.

Creatine is a natural compound in our bodies, predominantly in the muscles and brain.
It is vital in generating energy during intense workouts and heavy lifting.
Taking creatine supplements boosts the creatine levels in your muscles, leading to better workouts, bigger muscles, and increased strength.
As a result, many wonder, "Is creatine powder better than capsules?" This question is common among supplement users, and the answer depends on various factors such as convenience, absorption rates, and personal preference.
Additionally, understanding how long creatine stays in your body can help you decide about supplementation.
Typically, creatine can remain in the body for about a month after discontinuing use, with its levels gradually decreasing.
Supplementing with creatine can significantly enhance your performance and results, making it a popular choice among athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
Now that we have a basic understanding of creatine let's look at how it functions in the body and its essential roles.
Creatine Capsules are popular for their convenience and ease of use:
However, there are some drawbacks to consider:
On the other hand, Creatine Powder offers different advantages:
However, creatine powder does have its own set of cons:
The absorption rates and bioavailability of creatine can vary between the capsule and powder forms.
According to a study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, creatine powder is generally absorbed more quickly than capsules, allowing for faster availability in the bloodstream.
This can be particularly beneficial for athletes looking for immediate effects.
This scientific article provides more detailed insights into different creatine forms' absorption rates and bioavailability.
Below is a chart that summarizes the main differences between creatine powder and capsules.

Understanding these differences can help you choose the creatine form that best aligns with your fitness goals and lifestyle preferences.
Now that you know better let's find out how creatine works.
Numerous studies have shown the benefits of creatine supplementation.
For instance, a meta-analysis found it can significantly increase muscle strength and weightlifting performance.
Another study showed it can enhance power output during short-term, high-intensity exercises.
Creatine is a molecule produced in the body and found in various foods, particularly meat.
It plays a crucial role in energy production, especially in activities like weightlifting or sprinting.
Creatine helps your body produce energy quickly during intense workouts. It does this by restoring a molecule called ATP, which your muscles use for quick bursts of power.
This process lets you work out harder before feeling tired
This process is critical during high-intensity exercise, significantly increasing your muscles' work before fatigue.
A research paper in the Nutrients Journal offers a detailed examination of the molecular mechanisms associated with creatine supplementation.
The study highlights various biological processes and pathways impacted by creatine supplementation, indicating that its benefits may extend beyond merely enhancing energy levels during intense physical activity.
Here are some studies demonstrating the benefits of creatine supplementation on muscle performance and strength:
These studies collectively indicate that creatine supplementation is efficacious in improving muscle performance, strength, and recovery, making it a valuable addition to any fitness regimen.
Creatine powder vs. capsules for endurance athletes and bodybuilders are critical considerations for athletes looking to enhance their performance through supplementation.
Now that you know how creatine works and its benefits, let's figure out which form—powder or capsules—is best for your fitness goals.
Which one will best fit your routine and goals?
Let’s explore. Choosing between creatine powder and capsules can be pivotal based on your preferences, lifestyle, and fitness goals.
Here’s a practical guide to help you make an informed choice:
Choosing between creatine powder and capsules involves considering convenience, cost-effectiveness, dosage flexibility, absorption rates, and taste preferences to find the best option.
Now that you know the critical differences between creatine powder and capsules, let's delve into practical advice tailored to your goals and lifestyle.
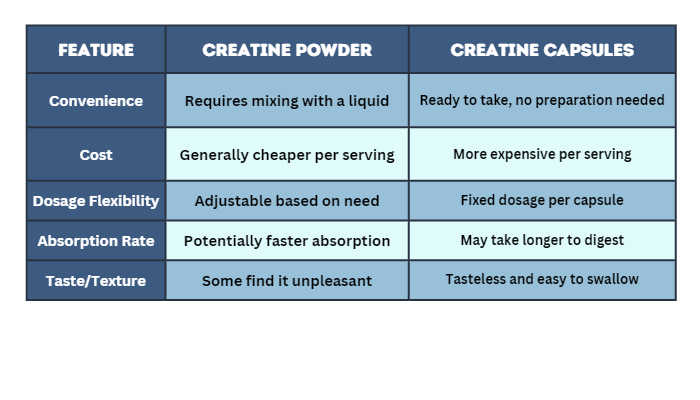
Using these considerations and resources, you can choose the creatine form that best aligns with your fitness goals and lifestyle.
By aligning your creatine form choice with your specific needs and lifestyle, you can maximize the benefits of your supplementation routine.
With these practical insights, let's explore why some prefer creatine powder over capsules.
Some may prefer creatine powder over capsules due to its versatility.
Powder allows for more flexible dosage adjustments, which can benefit individuals looking for precise control over their creatine intake.
Additionally, creatine powder can be easily mixed into various liquids, offering more consumption options.
Creatine powder's versatility and flexible dosage adjustments make it an attractive option for those seeking precise control over their supplementation.
While creatine powder has advantages, consider whether creatine capsules are equally effective.
Both creatine capsules and powder can be equally effective and high quality if taken as directed.
However, some individuals may find that capsules are less quickly absorbed than powder, which could impact their effectiveness in certain situations.
Ultimately, choosing capsules and powder depends on personal preference and lifestyle factors.
Creatine capsules can be as effective as powder if used correctly, though absorption rates may vary, making personal preference and lifestyle key deciding factors.
With a better understanding of the forms of creatine, let's delve into how creatine's benefits can enhance your fitness journey.
Creatine supplementation offers various benefits, particularly in enhancing exercise performance. Here are some of the benefits you can expect to enjoy:
Creatine supplementation significantly boosts muscle strength, improves high-intensity exercise performance, and enhances post-exercise recovery.
While creatine offers numerous benefits, it's essential to be aware of its potential side effects.
While creatine is generally well-tolerated and considered safe for long-term use, some individuals may experience side effects.
Before diving into those, it's important to note that these side effects are usually mild and manageable. These can include:
It's important to note that while these side effects can occur, they are relatively rare, and creatine is generally considered safe when used appropriately.
As with any supplement, it is always a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider before starting a new regimen.
While creatine is generally safe and well-tolerated, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort, water retention, and, in rare cases, kidney issues.
Understanding both the benefits and potential side effects of creatine is crucial, so let's now weigh the pros and cons of creatine capsules versus powder.
Creatine capsules offer a convenient, taste-free method of creatine supplementation, making them ideal for beginners.
They are also easy to take, which benefits those new to supplementation.
Additionally, creatine capsules are portable and require no mixing, so they are perfect for on-the-go use.
This allows users to avoid the taste of creatine powder entirely.
However, when deciding between creatine powder and capsules for beginners, creatine capsules are usually more expensive than powder.
The body may also not absorb them as quickly as the powder form.
Additionally, capsules allow you to fine-tune your dosage slowly, while powder does not.
These factors may influence your decision when choosing the best product for beginners or general supplementation.
Understanding the pros and cons of creatine capsules versus powder is crucial when considering creatine supplementation.
Here is a quick summary:
Pros of Creatine Capsules:
Cons of Creatine Capsules:
Pros and Cons of Creatine Powder:
Now that you know why creatine is important, let's compare the pros and cons of capsules and powder to help you decide which is better for you.
When considering the best creatine form for muscle gain, convenience, absorption rates, and potential side effects must be considered.
A comparison of creatine supplements reveals that some users prefer the convenience of creatine capsules, which can be quickly taken on the go without mixing.
However, creatine powder offers more versatility in dosage adjustment and can be easily mixed with liquids of your choice.
Additionally, research suggests that creatine monohydrate, found in capsule and powder forms, is the most studied and effective form of creatine for muscle gain.
Following recommended dosages and staying hydrated while using creatine are essential to maximize its benefits and minimize potential side effects.
Ultimately, the best creatine form depends on your individual preferences and lifestyle. Experimenting with capsules and powder can help determine which form works best for you.
When comparing creatine pills vs powder for workouts, consider your workout routine, convenience, and personal preferences to make an informed decision.
Whether you choose capsules or powder, incorporating creatine into your fitness regimen can help you achieve your muscle gain goals.
Consider absorption rates and personal preferences when determining which creatine form is better for muscle growth.
With a clear understanding of how each creatine form can impact your muscle gain goals, let's explore who can benefit most from incorporating creatine into their fitness regimen.
Creatine benefits anyone looking to improve strength, power, and high-intensity exercise performance.
This includes athletes, bodybuilders, and recreational gym-goers. It can also benefit older adults looking to maintain muscle mass and strength.
Additionally, when creatine is coupled with a high-calorie meal, it can further enhance results.
While creatine can offer significant benefits for various individuals, it’s crucial to identify who should avoid it to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Let’s explore who might need to be cautious about using creatine.
Although creatine is considered safe for most individuals, those with kidney disease or at risk of kidney issues should refrain from supplementation.
It is always advisable to seek guidance from a healthcare professional before initiating any new supplement regimen.
With a clear understanding of who should avoid creatine, it’s important to compare how creatine stacks up against other supplements to determine its relative effectiveness and benefits.

Creatine is often compared to other performance-enhancing supplements, such as beta-alanine and branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs).
While these supplements can also enhance exercise performance, creatine is unique in its ability to rapidly produce ATP, making it particularly beneficial for high-intensity exercise.
Having explored how creatine compares with other supplements, let's now delve into the different varieties of creatine to help you find the one that best suits your needs.
When considering creatine supplementation, understanding the options available to you is essential. Here are a few of the commonly used options:
This form of creatine is the most extensively researched and commonly used.
Numerous studies support its safety and efficacy.
Any new forms of creatine must be compared to creatine monohydrate before they can be recommended.
Some manufacturers suggest that creatine ethyl ester is superior to other forms of creatine, including monohydrate.
Some evidence indicates that the body may more effectively absorb it than creatine monohydrate.
However, a direct comparison study found it less effective at increasing creatine levels in the blood and muscles.
Creatine HCL has gained considerable popularity with some manufacturers and supplement users. Initial excitement about it was probably due to reports of its superior solubility.
However, this theory is only speculation until it is tested.
One study found that creatine HCL was 38 times more soluble than the monohydrate form.
Certain supplement manufacturers have introduced a buffered form by adding an alkaline powder to enhance creatine's stability in the stomach.
His formulation aims to increase potency and alleviate side effects like bloating and cramping.
However, a study directly comparing buffered and monohydrate forms found no discernible differences in effectiveness or side effects.
While most creatine supplements are powdered, some are available as ready-to-drink solutions in which the supplement is already dissolved in water.
Limited research on liquid forms suggests they may be less effective than monohydrate powders.
Creatine magnesium chelate is a supplement that's chelated with magnesium.
This means that magnesium is attached to the creatine molecule.
One study compared bench press strength and endurance between groups consuming creatine monohydrate, creatine magnesium chelate, or a placebo.
The monohydrate and magnesium chelate groups improved their performance more than the placebo group but did not differ.
With a comprehensive overview of the different creatine varieties, let's summarize their key features to make selecting the best option for your needs easier.
Here is a quick summary chart of the different forms:
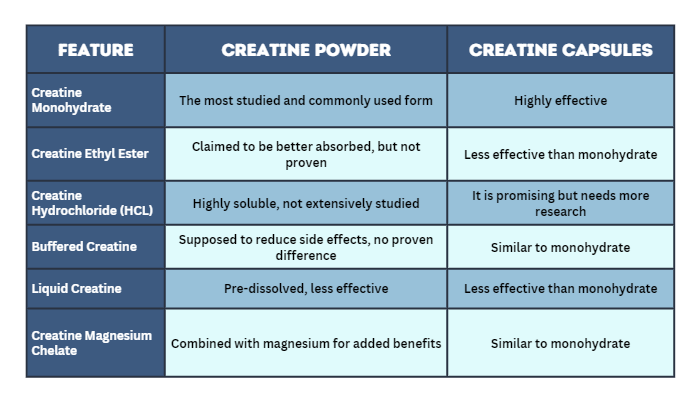
With this overview of different creatine options, you can make an informed choice based on their specific benefits and effectiveness.
Let us help you select the best creatine form to meet your individual needs.
Creatine is a captivating supplement with wide-ranging benefits, catering to fitness enthusiasts, professional athletes, and beginners.
Our bodies synthesize this naturally occurring compound, which can be sourced from foods like meat and fish.
Supplementation offers many advantages, including boosted strength, muscle development, and enhanced brain function.
The recommended dosage for creatine is typically 5 grams per day. Some individuals may choose to do a "loading phase" where they take 20 grams of creatine daily for 5-7 days, but this is unnecessary.
Yes, doing so can help maintain your muscle stores of creatine.
Research has shown that creatine is safe for long-term use when taken at recommended dosages.
Yes, creatine is safe and effective for women and men.
We've covered a lot of ground, so let's wrap up with the final verdict on whether creatine capsules or powder is the best choice for you.
Choosing between creatine capsules and powder depends on personal preference and lifestyle requirements.
Both forms effectively boost muscle creatine levels and enhance workout performance.
Expert Advice: Before starting any new supplement...
Before incorporating any new supplement, including creatine, into your routine, seek guidance from a healthcare professional.
Enhanced Fitness Support:
With its demonstrated advantages and safe usage, creatine is a beneficial addition to fitness enthusiasts' supplement regimens.
Following this comprehensive guide, you should be well-equipped to choose the correct form of creatine for your needs.
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Ready to see the results?
Start incorporating the right creatine form into your fitness routine today.



Useful Links
 About FitFrek
About FitFrekFitFrek operates as an independent platform, offering comprehensive workouts, programs, routines, guides, and unbiased reviews to accelerate your progress. We pride ourselves on our honesty, delivering straightforward and candid insights. FitFrek does not offer medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment services.